Author: FinTax
Original link: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/L43fUJiS6OmliYZg0uH6Kw
Disclaimer: This article is a reprint. Readers can find more information by following the original link. If the author has any objections to the reprint format, please contact us and we will modify it to suit the author's request. This reprint is for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice or represent the views or positions of Wu Blockchain.
Original link: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/L43fUJiS6OmliYZg0uH6Kw
Disclaimer: This article is a reprint. Readers can find more information by following the original link. If the author has any objections to the reprint format, please contact us and we will modify it to suit the author's request. This reprint is for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice or represent the views or positions of Wu Blockchain.
News Overview
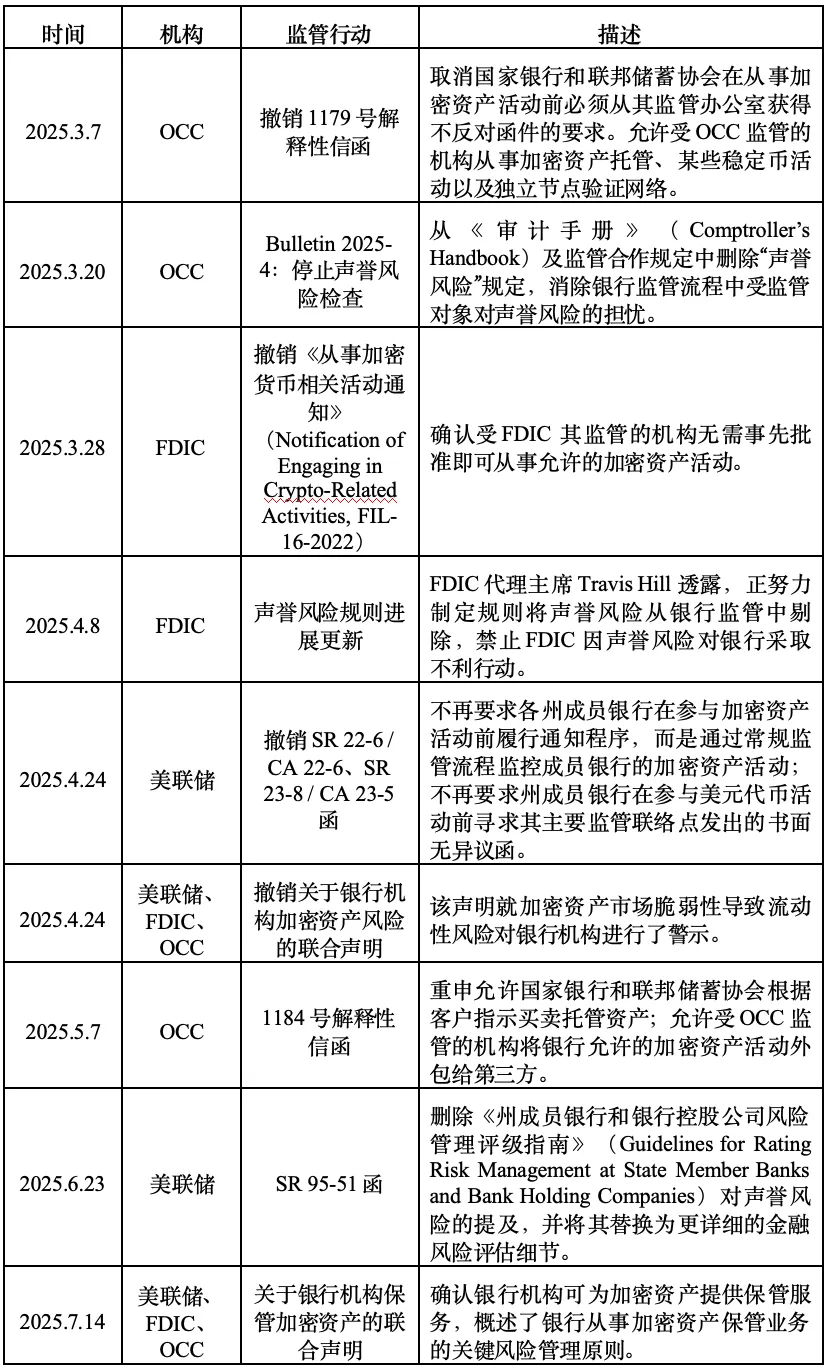
On July 14, 2025, the Federal Reserve, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) reportedly issued a joint statement (hereinafter referred to as the "Statement") providing guidance to banks on how to provide crypto asset custody services to clients. This is the latest move by Trump-era regulators as they weigh how traditional lenders should engage with the digital asset business. The Statement states that banks considering providing custody services for crypto assets should consider the evolving nature of the crypto market, including the technology behind it, and must implement a risk management framework that is appropriately adapted to the associated risks.
The move comes after regulators in April withdrew their previous guidance on the risks of the crypto industry, freeing lenders to offer products and services more freely to clients trading digital assets. At the time, the Fed also rescinded a 2022 directive requiring banks to provide advance notice of crypto asset activity.
FinTax Review
1. Statement Content: Six Key Risks of Bank Crypto Custody
The joint statement lists a series of existing laws, regulations, guidance and risk management principles related to the provision of crypto asset custody services, highlights various risk management, legal and compliance risks, and elaborates on relevant mitigation measures. The statement is divided into six parts:
(1) General Risk Management Considerations: Banking institutions should consider potential risks before providing crypto asset custody services. Effective risk assessments should address the institution's core financial risks, its ability to understand asset classes, its ability to ensure a strong control environment, its contingency plans, and its employees' necessary knowledge of crypto asset custody, so as to provide services in a safe and sound manner. In addition, banking institutions providing custody services for crypto assets should also consider the ever-changing nature of the crypto asset market and establish a risk governance framework that can appropriately adapt to such changes.
(2) Encryption key management: The loss or leakage of encryption keys or other sensitive information is one of the main risks of crypto asset custody. Banking institutions should have control over crypto assets, that is, they should reasonably prove that no other party can obtain information sufficient to transfer crypto assets outside the control of the banking institution. Such control standards should also apply to the banking institution's sub-custodian. In addition, banking institutions should also consider how to securely generate encryption keys, develop contingency plans in the event of key loss or leakage, and make their network security environment a focus of risk management.
(3) Other risk management considerations: Different types of crypto assets require different key management solutions, or may have software or hardware requirements that banks lack experience or capabilities to handle. The potential risks associated with different account models may also vary. Therefore, while banking institutions follow standard custody risk management principles, they also need to make adjustments based on the specific custody services they provide.
(4) Legal and compliance risks: First, like other banking activities, crypto asset custody activities are subject to the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Counter-Terrorism Financing (CFT), and the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC). Second, changes in the regulatory environment for crypto assets also bring higher compliance risks. Banking institutions should ensure that related activities comply with all applicable laws and regulations. Finally, customers may misunderstand the role of banking institutions in custody arrangements, which may lead to risks. This requires banks to provide customers with clear, accurate, and timely information about their custody activities to reduce such risks. At the same time, banking institutions should also comply with applicable recordkeeping and reporting requirements.
(5) Third-party risk management: "Third-party risk" refers to the risk posed by sub-custodians or other service providers (e.g., technology providers, cash management institutions) with whom banking institutions work. Banking institutions are responsible for the activities performed by their sub-custodians according to their terms and conditions. Therefore, banks should conduct sufficient due diligence, including assessing the sub-custodian's key management solution, its compliance with custody risk management principles, its handling of customer assets in the event of bankruptcy or operational failure, and the adequacy of its risk management and recordkeeping. For other service providers, banks should weigh the risks of purchasing third-party software or hardware against the risks of maintaining such software or hardware as a service.
(6) Audit requirements: Audit procedures are essential for effective risk management and internal control. Therefore, the audit procedures of banking institutions should appropriately cover crypto asset custody services (including third-party risk management), focus on risks unique to crypto asset custody, such as key generation, storage and deletion, transfer and settlement of crypto assets, the adequacy of relevant information technology systems, and assess the ability of employees to identify and control crypto asset risks. If a banking institution lacks audit expertise, it should engage an appropriate independent third party to conduct the audit.
2. Policy Background: Trump Promotes Crypto Regulatory Reform
The joint statement comes against this backdrop, as the US government's stance on crypto assets has shifted significantly since Trump's second term. Over the past few months, several US banking regulators have taken a series of actions, reversing various interpretive letters and regulatory statements related to crypto assets issued during the Biden era. One significant move was the removal of "reputational risk" assessments from regulatory procedures, replacing the vague concept of reputational risk with more specific financial risk categories. This move effectively prevented regulators from pressuring banks to refuse to serve crypto companies, helping to alleviate banks' real concerns about servicing controversial sectors like crypto assets.
Another significant move is the removal of the prior notification requirement for engaging in crypto-asset-related activities. Previously, banks were required to obtain a written "no-objection letter" from regulators before engaging in crypto-asset-related activities. Now, banks' crypto activities will no longer be subject to this process and will instead be monitored through regular regulatory procedures.
In addition, various bank regulators have also restored previous regulatory policies that conflicted with the Biden administration's regulatory philosophy. For example, the OCC once again allowed its regulated entities to buy and sell custody crypto assets according to customer instructions, and allowed them to outsource custody and execution services to third parties on the premise that the third parties can properly manage risks.

After taking office, Trump reversed the previous administration's guidelines urging banks to exercise caution in the crypto sector and implemented comprehensive crypto asset regulatory reforms. This was a fulfillment of his political commitment and a key initiative to establish the United States as the world's "crypto capital" and stimulate innovation and development in the U.S. economy. The joint statement released today forms part of the U.S. crypto asset regulatory reforms. It marks that after abandoning several law enforcement-focused regulatory policies to unleash market vitality, the U.S. government has begun to guide banks and other entities to participate in crypto asset activities in a compliant, safe, and stable manner by refining regulatory rules and strengthening business guidance, supporting the innovative development of the crypto industry. More crypto-friendly statements may be issued in the future.
3. Significance and Outlook: The Future of Bank Crypto Custody Regulation
Overall, the statement discusses how existing laws, regulations, and risk management principles apply to the custody of crypto assets. It aims to provide guidance to banking institutions that provide or consider providing crypto asset custody services. It reflects a more relaxed regulatory stance, but still emphasizes that banking institutions should strictly control risks in crypto asset custody activities and abide by core principles such as safety, soundness, and consumer protection, reflecting the regulatory bottom line of the U.S. banking regulatory authorities in the crypto industry.
For banks currently engaged in or considering crypto-asset custody, the statement provides an entry point into the crypto-asset custody market, creating new opportunities for those with appropriate risk management capabilities and robust governance structures. Furthermore, the statement provides specific guidance on risk management for banks already engaged in crypto-asset custody. Regulatory oversight will continue to prioritize compliance and security across operational, legal, and financial aspects. According to the statement, banks may need to adjust product rules and internal policies and procedures to reflect the unique risks and compliance obligations of crypto-asset custody, such as improving cybersecurity protocols and key management systems, and conducting regular security testing.
It is important to note that while the statement provides some clarity, the regulatory and legal landscape at both the federal and state levels remains uncertain in the context of the government's crypto regulatory reforms. Simply meeting the elements of the statement may not fully meet regulatory requirements. Banks must maintain ongoing communication with regulators at all levels and maintain good compliance records in preparation for rigorous regulatory scrutiny.
From a longer-term perspective, the refinement of US crypto custody regulations may attract more crypto asset companies to return to or enter the US, driving innovation and development in the US blockchain industry. As traditional financial institutions increasingly engage with the crypto asset sector, and related services like crypto asset custody are incorporated into the existing regulatory framework, financial activities related to crypto assets will flourish in a safer and more regulated environment.







